Earth Wire
An Earth Wire, also known as a grounding wire, is a conductor that provides a direct path for electrical fault currents to safely dissipate into the ground. It is a crucial component of electrical safety, protecting people and equipment from electric shock and damage.
Features
- Made from high-conductivity materials such as copper or aluminum.
- Insulated or bare, depending on the application.
- Available in various thicknesses to handle different electrical loads.
- Corrosion-resistant for long-lasting performance.
Applications
- Used in electrical installations for safety grounding.
- Protects electrical appliances and systems from surges and faults.
- Essential in power transmission lines to prevent lightning damage.
- Used in household, industrial, and commercial electrical systems.
Types of Earthing Chemicals
An Earth Wire, also known as a grounding wire, is a conductor that provides a direct path for electrical fault currents to safely dissipate into the ground. It is a crucial component of electrical safety, protecting people and equipment from electric shock and damage.
Functions
- Reduces soil resistivity and improves grounding effectiveness.
- Enhances the lifespan of earthing electrodes.
- Ensures stable electrical grounding in various soil conditions.
- Minimizes voltage fluctuations and electrical hazards.
Applications:
- Bentonite - A clay-based material that retains moisture and improves conductivity.
- Graphite Powder - Used to enhance the longevity and performance of earthing electrodes.
- Charcoal & Salt - Traditional earthing materials that help maintain soil conductivity.
- Conductive Gel - A specialized compound that improves electrode performance.

Earth Electrode
An Earth Electrode is a conductive element (such as a rod, plate, or strip) buried in the ground to provide a low-resistance path for electrical fault currents to dissipate safely into the earth. It is a crucial component of an earthing system, ensuring electrical safety and stability.
Types of Earth Electrodes
- Rod Electrode - A metal rod (copper or galvanized steel) driven into the ground.
- Plate Electrode - A metal plate (copper or GI) buried at a specific depth.
- Strip Electrode - A long metal strip or wire buried in a trench.
- Pipe Electrode - A hollow pipe (GI or copper) placed vertically in the ground.
Functions
- Provides a safe path for fault currents.
- Reduces electrical shock hazards.
- Maintains system voltage stability.
- Protects electrical equipment from lightning and surges.

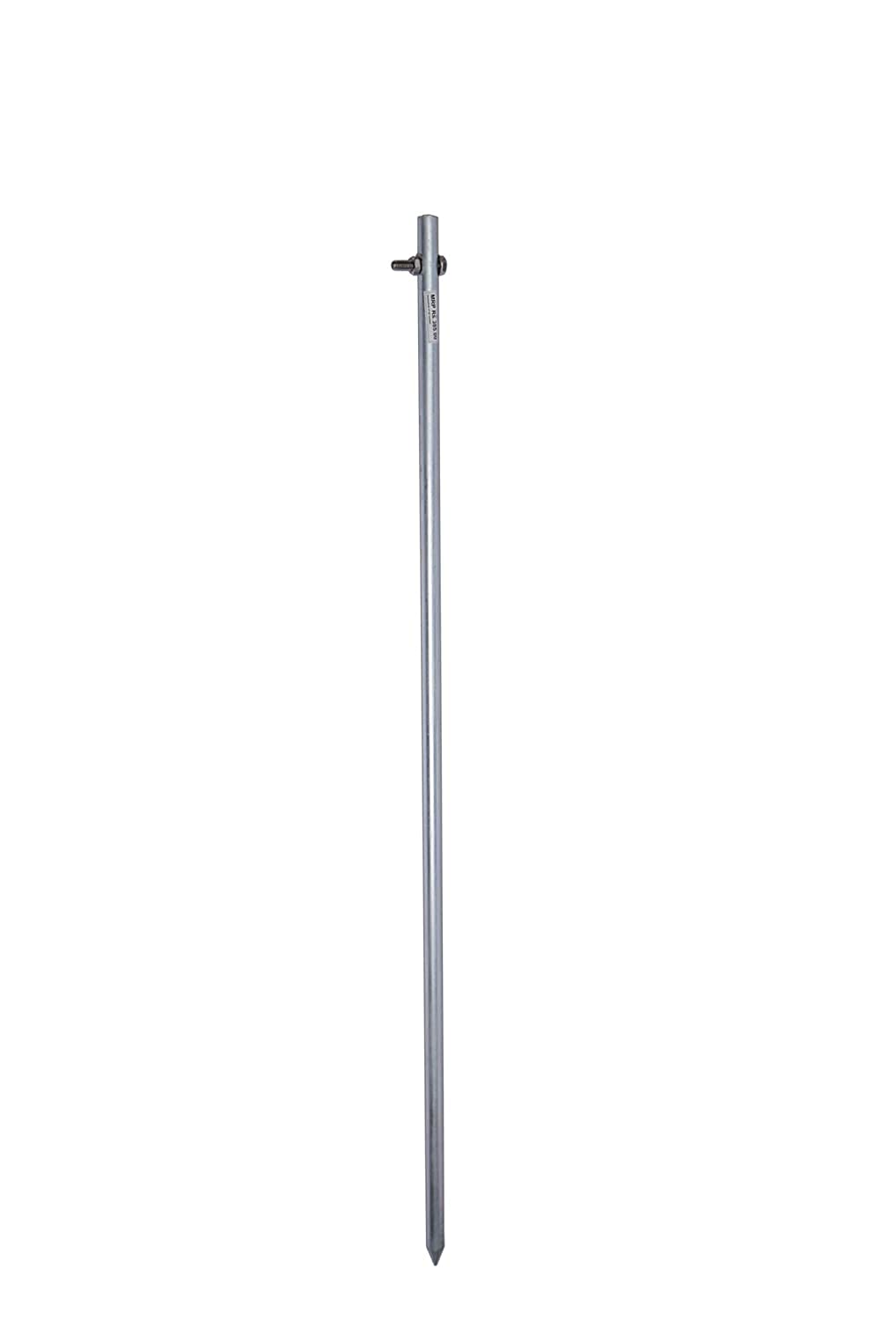
Earth Rod
An Earth Rod is a metal rod, typically made of copper, galvanized steel, or stainless steel, driven into the ground to provide a low-resistance path for fault currents to dissipate safely into the earth. It is a fundamental component of grounding systems in electrical installations.
Types of Earth Rods
- Copper-bonded Rods - Steel rods coated with copper for corrosion resistance.
- Galvanized Steel Rods - Steel rods coated with zinc for cost-effective grounding.
- Solid Copper Rods - Highly durable and corrosion-resistant, used in critical applications.
- Stainless Steel Rods - Used in environments with extreme soil conditions.
Functions
- Provides a safe path for electrical fault currents.
- Reduces the risk of electric shock and equipment damage.
- Enhances system voltage stability.
- Protects electrical installations from lightning and surges.

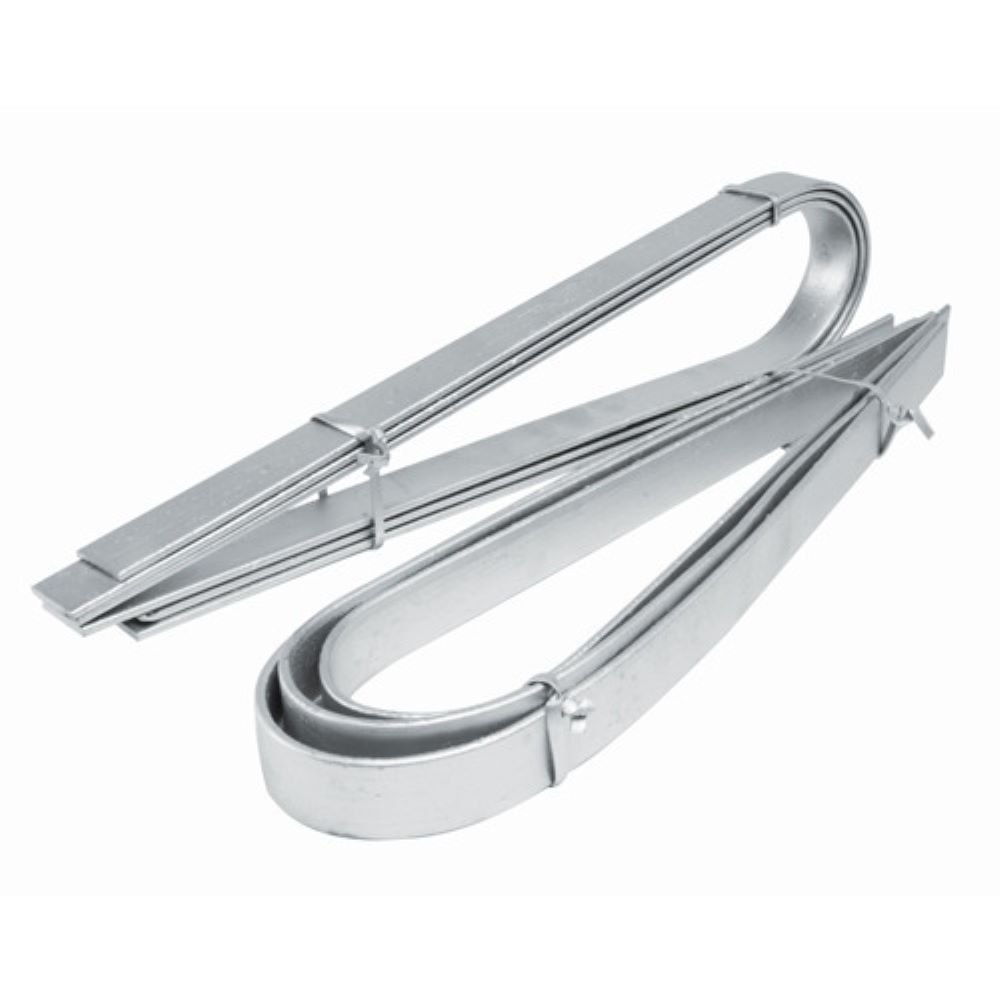
GI Earthing Strip
A GI (Galvanized Iron) Earthing Strip is a flat, galvanized iron conductor used in grounding systems to provide a safe and efficient electrical discharge path. It ensures the dissipation of fault currents into the ground, protecting electrical equipment and personnel from electrical hazards.
Features
- Made of high-quality galvanized iron for corrosion resistance.
- Available in various thicknesses and widths as per electrical requirements.
- Durable and long-lasting in harsh environmental conditions.
- Easy to install and maintain.
Applications
- Used in electrical grounding systems for buildings and industrial plants.
- Provides effective grounding for transformers, generators, and panels.
- Ensures safe discharge of fault currents in power distribution networks.
- Used in lightning protection systems for enhanced safety.

Earthing Insulator
An Earthing Insulator is a non-conductive material or device used in electrical grounding systems to prevent unintended current flow and enhance safety. It isolates electrical components from direct contact with the ground, ensuring proper insulation and protection against electrical faults.
Types of Earthing Insulators
- Porcelain Insulators - Used in high-voltage applications due to their excellent insulating properties.
- Composite Insulators - Made of polymeric materials for durability and weather resistance.
- Glass Insulators - Offer high mechanical strength and resistance to environmental conditions.
- Rubber & Plastic Insulators - Commonly used in low-voltage and household electrical systems.
Applications
- Used in power transmission lines to prevent electrical leakage.
- Ensures safety in grounding systems by preventing unintended contact.
- Protects electrical devices from voltage fluctuations and short circuits.
- Common in industrial, commercial, and residential electrical installations.


